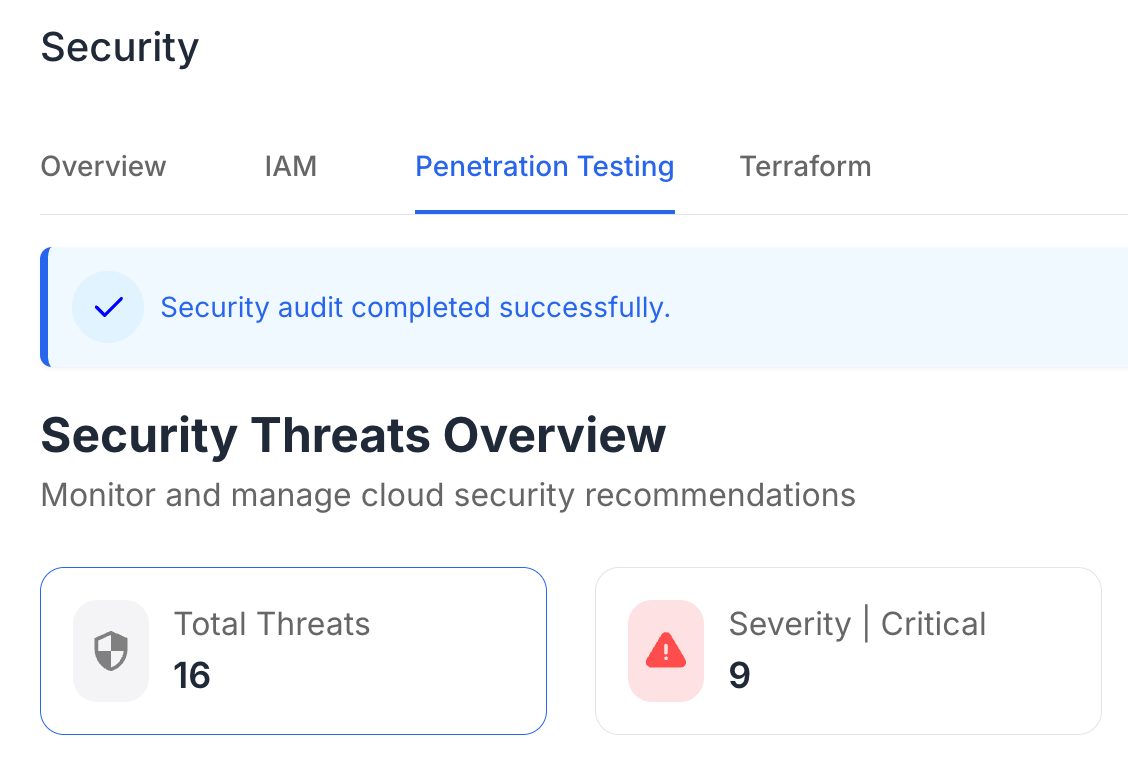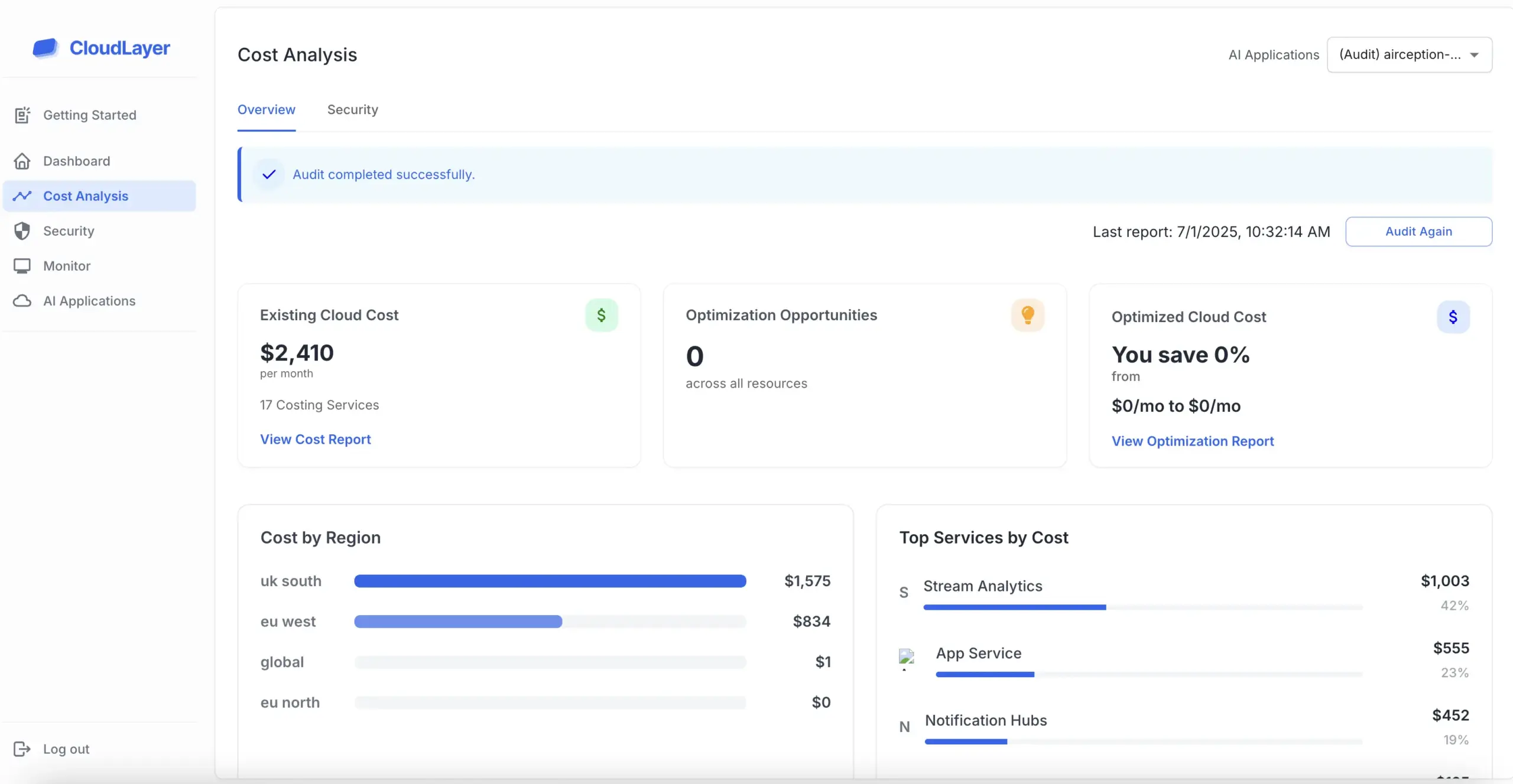

The HIPAA Privacy Rule, established under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, sets national standards for protecting sensitive patient information. It governs how healthcare entities manage and share personal health information (PHI).
Among its key provisions, the HIPAA Privacy Rule mandates that healthcare providers obtain patient consent before disclosing any PHI. Additionally, it outlines the rights patients have regarding their own health information, including the right to access their records.
Compliance with the HIPAA Privacy Rule is required for covered entities, which include healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses. Business associates that handle PHI on behalf of these entities must also adhere to the rule’s requirements.
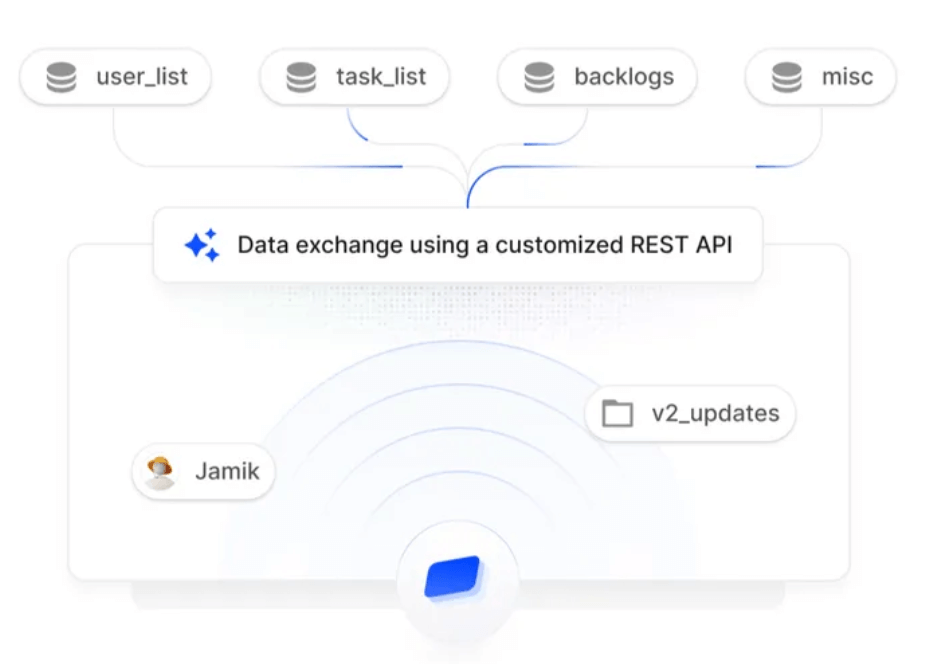
Failure to comply with the HIPAA Privacy Rule can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and legal repercussions. Organizations may also face reputational damage that can impact their trustworthiness in the eyes of patients.