HIPAA, enacted in 1996, was designed primarily to improve the efficiency of the healthcare system while ensuring the privacy and security of patient information. The act comprises several provisions, including the Privacy Rule, which establishes national standards for protecting individuals’ medical records and personal health information.
Compliance with HIPAA involves several key components, including the Administrative Safeguards, Physical Safeguards, and Technical Safeguards. Administrative Safeguards encompass policies and procedures to manage the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of security measures.
The Privacy Rule is a fundamental aspect of HIPAA that governs how healthcare providers, plans, and clearinghouses handle protected health information (PHI). This rule gives patients rights over their health information, including the ability to access their records and request corrections.
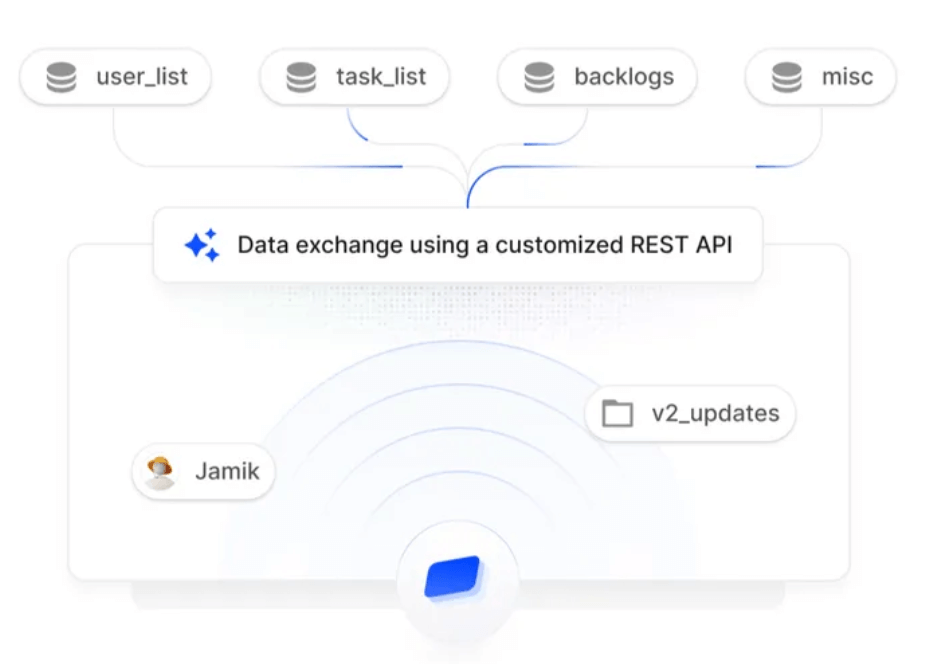
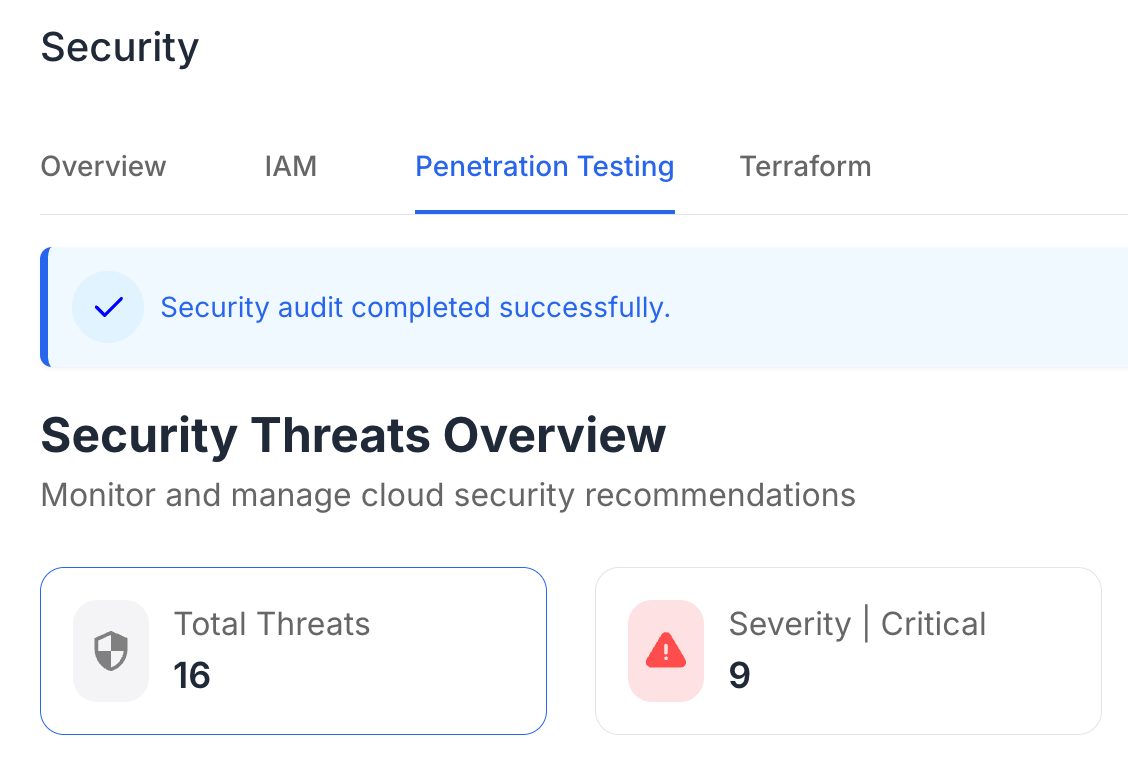
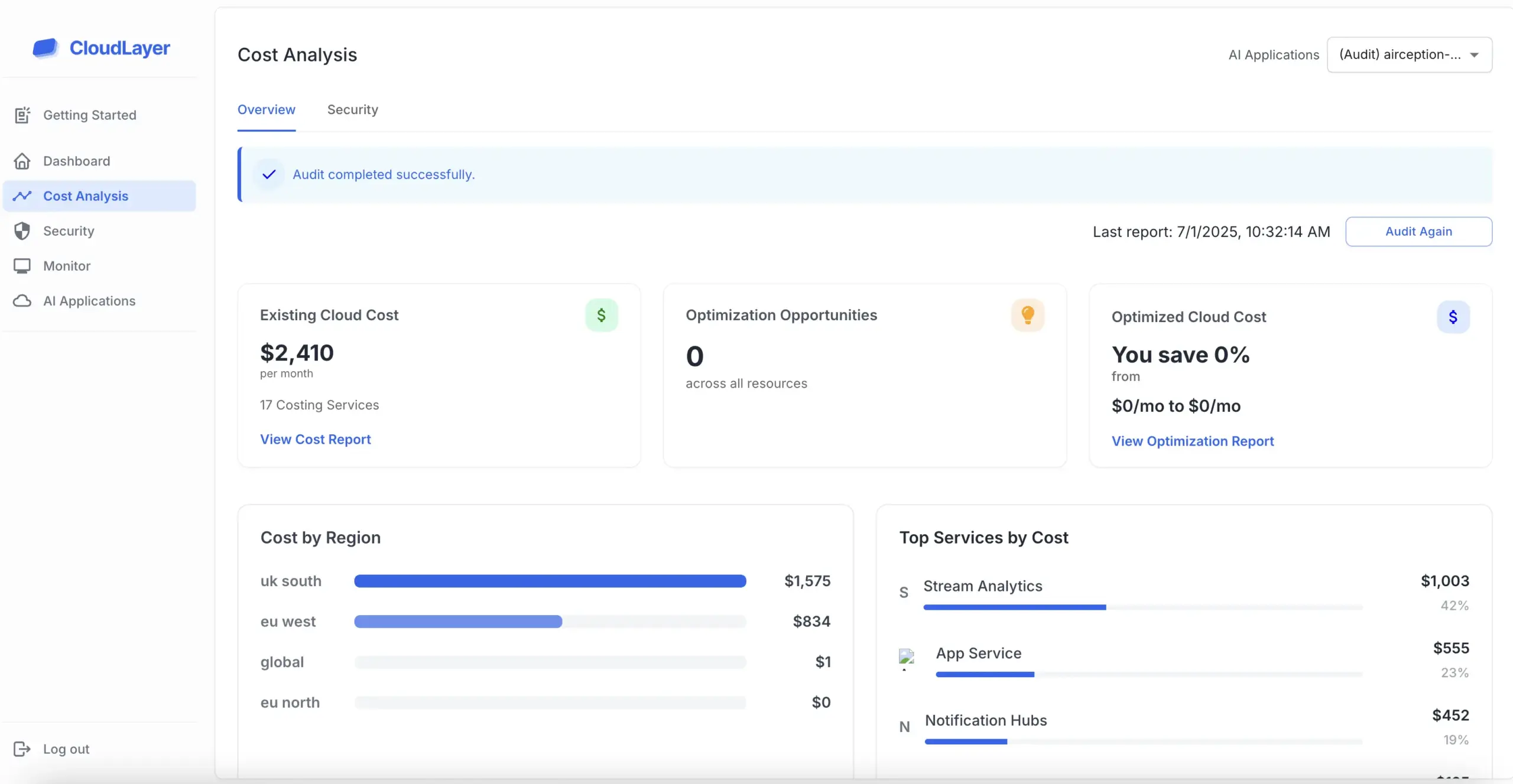
Failing to comply with HIPAA can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines and legal ramifications for healthcare entities. Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can also damage an organization’s reputation, eroding patient trust and leading to a loss of business.